Climate Change and Our Role In It Made Simple
What is Climate Change?
You probably hear the term Climate Change on a regular basis, but what does it actually mean? What are the basics of Climate Change?
Put simply, it is the change in average weather conditions over an extended period of many years. This includes temperature, rainfall, humidity and storm conditions.

So how do we know the climate is changing?
Using geological records we are able to study the planet’s past climate conditions. This information is in turn used understand how it has changed, what has driven this change and what could happen in the future.
How is our climate changing?
The climate has fluctuated greatly across the Earth’s history. It has experienced periods significantly warmer that we experience today, as well as much colder periods, known as ice ages.
Today, there is an indisputable body of evidence to prove the climate is changing.
Temperatures have risen 1.2oc since 1990. This in turn is causing rainfall patterns to change, glaciers and polar ice caps to begin melting and habitat ranges in the natural to shift.

Temperature – Where are we heading?
The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) advise increases should be limited to 1.5oc to stem the most impactful forms of potential climate change.
However, we are currently on track to reach an increase of 2.7oc. This could result in damaging impacts.

What is causing this change?
The core driver for Earth’s climate, at least for the last several hundred thousand years, has been the amount of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. Human activity has led to the increase of 6 key GHGs:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Ozone (O3)
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Water Vapour (H2O)

The Greenhouse Effect
When sunlight hits the Earth, some is absorbed and then emitted back out as heat. The GHGs listed above trap some of this heat and prevent it heading back out into space.
Consequently, more heat is retained and planet begins to warm. This is called the greenhouse effect.
Historically, this effect has allowed the planet to stay warm enough for us to live here, but too much can shift temperatures to a less habitable climate.
Today we are beginning to see the early impacts of increasing GHGs in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide. This is causing a rise in temperatures and in turn the climate to begin changing.
The Role of human activities in climate change
Much of what we rely upon is currently made possible by fossil fuels: oil, gas and coal. From powering our homes to driving cars and producing the food we eat, they all largely rely on fossil fuels.
Fossil Fuel Use

Burning of these fossil fuels releases GHGs, particularly Carbon Dioxide (CO2). In fact doing so has increased the volume of CO2 in our atmosphere by over 50% since 1850.
This CO2 remains in the atmosphere for up to 1000 years once released, making long term accumulation a major risk.
Harm to Natural Habitats
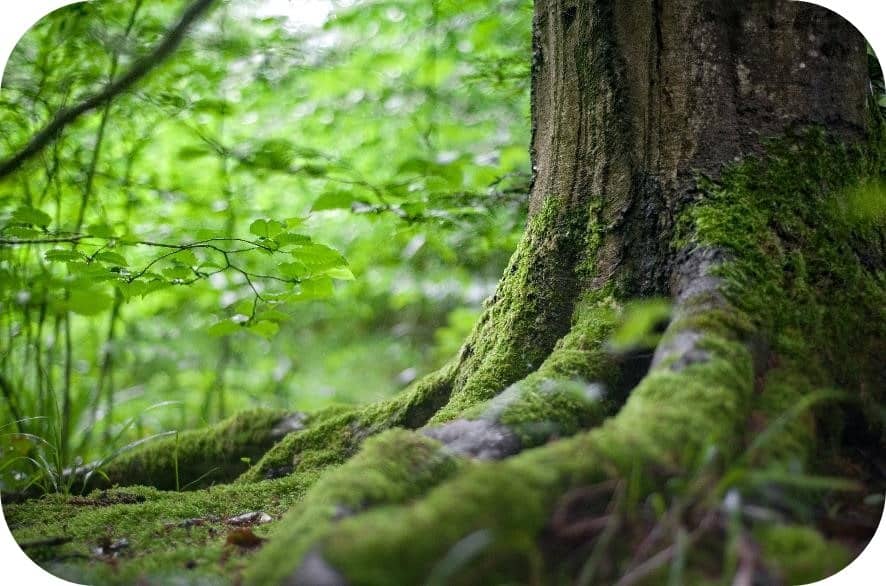

Aside from burning fuel, human activity is degrading natural habitats, such as forests.
Natural habitats play a role in the natural climate balance by absorbing carbon dioxide. When these habitats are damaged the amount of carbon they absorb is reduced.
Identifying the Impact
The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (the IPCC) is coordinating the global scientific effort to understand how climate change is impacting us and the likely scenarios we face in the future.
It’s based on these studies that we are globally beginning to take action.

How can we bring climate change under control?
Global Action
Climate change is a global issue, requiring successful international cooperation to resolve. What this means is different for different countries.
Some countries are more reliant on fossil fuels than others. Some are in poorer economic positions to pursue the technologies that can replace fossil fuels.

The UN coordinates an ongoing series of climate conferences, known as COPs, to ensure countries around the world are taking action and cooperating.
Under current agreements, these conferences have seen the majority of the world’s countries sign up to Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Net Zero
Collectively, NDCs support reaching a Net Zero position. This significantly reduces the emissions our activities cause.

Remaining emissions would be offset by carbon sequestration, absorbing emissions from the atmosphere through natural and mechanical means.
Renewable Energy

Renewable energy will be a vital part of action to reach net zero and limit climate change. Renewables provide energy through natural sources, such as solar and wind, without a direct fossil fuel emission.
Their supply is sometimes erratic and therefore support from battery storage facilities, as well as increased nuclear power production, is necessary.
Additional actions include shifting away from combustion engine vehicles to electric ones, and reducing waste of materials.
The Role of Nature

Ensuring the natural world is supported and preserved as climate change takes effect is also critical.
Aside from the intrinsic value of preserving nature, natural systems provide us with the water and soils needed for human survival, as well as absorbing some of the emissions we continue to release.
Put simply if we wish to thrive then so must nature.

How can we all play our part?
There are a range of actions we can all take. From changing small things individually in our daily lives and homes, to embedding sustainable practice into the businesses we run.
Best of all, many of these changes are actually more efficient in the long run, helping to save on daily costs and make businesses more profitable.
You can learn more about taking action through some of the below articles here at Greener Insights. Key green terms are also explained here to help make things clear and simple.

We’re also working on a range of tools that can help you with the practicalities of taking action, which we’ll share more about with you over the coming months!







